No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
In the [http://www.physics.queensu.ca/~robbie/equipmentusage.html Material Physics Cleanroom] (located in Stirling Hall at [http://www.queensu.ca Queen's University]), a Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope is often used for imaging and characterization purposes. A {{wp|scanning electron microscope}} uses an electron beam to obtain high levels of magnification and resolution for imaging. The specific type of FESEM found in the Materials Physics Cleanroom is the Leo/Zeiss 1530 Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope<ref name="one"> Material Physics Analytical Services. Material Physics Cleanroom, Queen's University. http://www.physics.queensu.ca/~robbie/equipmentusage.html </ref>. | In the [http://www.physics.queensu.ca/~robbie/equipmentusage.html Material Physics Cleanroom] (located in Stirling Hall at[http://www.queensu.ca Queen's University]), a Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope is often used for imaging and characterization purposes. A {{wp|scanning electron microscope}} uses an electron beam to obtain high levels of magnification and resolution for imaging. The specific type of FESEM found in the Materials Physics Cleanroom is the Leo/Zeiss 1530 Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope<ref name="one"> Material Physics Analytical Services. Material Physics Cleanroom, Queen's University. http://www.physics.queensu.ca/~robbie/equipmentusage.html </ref>. | ||
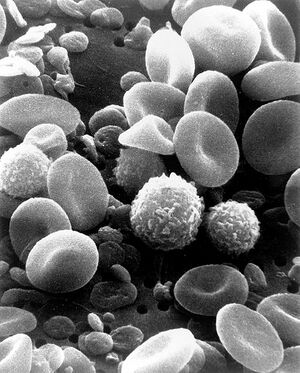
[[Image:SEM_Blood_Cells.jpg|thumb|right|Figure 1. SEM image showing circulating human red blood cells. Note that a SEM image is always a grayscale image (colors can be artificially added). The depth of field seen is typical of an SEM.]] | [[Image:SEM_Blood_Cells.jpg|thumb|right|Figure 1. SEM image showing circulating human red blood cells. Note that a SEM image is always a grayscale image (colors can be artificially added). The depth of field seen is typical of an SEM.]] | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 24 July 2009
Introduction
In the Material Physics Cleanroom (located in Stirling Hall atQueen's University), a Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope is often used for imaging and characterization purposes. A W uses an electron beam to obtain high levels of magnification and resolution for imaging. The specific type of FESEM found in the Materials Physics Cleanroom is the Leo/Zeiss 1530 Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope[1].
Microscope Specifications
- Schottky field-emission electron source
- Operating voltage: 0.2 - 30 kV
- Rated resolution: 1.2 nm at 20 kV , 2.5 nm at 5 kV, and 3 nm at 1 kV[2]
Protocol
- Working with the FESEM requires a trained lab researcher at all times.
- The lab researcher will assist in all of the imaging aspects and can offer helpful advice and guidance.
- The actual FESEM operation will be done by the researcher. A general outline of how the imaging program operates can be seen on this Georgia Tech College of Engineering page[3]
- Samples should be clean, prepared and free of debris before imaging. Some samples may require conductive coatings in order for the electron beam to properly image the subject.
Tips
- Be familiar with the general cleanroom procedures before entering. The dress attire conists of a cleanroom lab coat and booties.
- Always work with a qualified lab researcher unless proper training has been covered.
- If a cross sectional view is desired, ensure a clean break can be found (use a diamond scribe) on the sample and mount the sample in such an orientation that one edge slightly hangs off of the round holder.
- Double check sample identifications, sample placements and sample orientations before placing the samples inside the FESEM chamber.
Other Equipment in the Materials Physics Cleanroom
- X-Ray diffraction: Philips X'Pert XRD
- W: Digital Instruments Multimode Nanoscope AFM
- Variable angle Spectroscopic W
For all booking information, rates and schedules, please see the Materials Physics cleanroom page.
Sources and Citations
- ↑ Material Physics Analytical Services. Material Physics Cleanroom, Queen's University. http://www.physics.queensu.ca/~robbie/equipmentusage.html
- ↑ Characterization Equipment: Leo 1530 Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope. National Nanotechnology Infrastructure Network at Penn State. http://www.mri.psu.edu/facilities/NNIN/Equipment/EquipmentLEO1530FESEM.asp
- ↑ LEO 1530 Thermally-Assisted Field Emission (TFE) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Tech College of Engineering. http://www.mse.gatech.edu/Research/Equipment_Facilities/CNC/LEO_1530/leo_1530.html
<layout name="Howtos" />