Source
- Denkenberger, D.C., Brandemuehl, M.J., Pearce, J.M., Zhai, J. Expanded Microchannel Heat Exchanger: Nondestructive Evaluation. Heat Transfer Engineering 40(20)1671-1679, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/01457632.2018.1496976 open access
Abstract
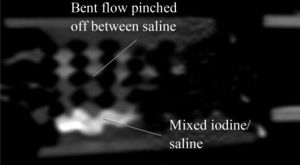
Recent theoretical developments in expanded microchannel polymer-based heat exchangers were promising, but the initial experiments underperformed simple theory. In order to understand this discrepancy, this paper introduces a nondestructive methodology for characterizing polymer heat exchangers. A computerized tomography (X-ray) scan was performed to diagnose the problem. The method was tested on the expanded microchannel polymer heat exchanger to determine the variations in geometry between the theoretical and experimental heat exchanger. Channels were found to have variable heights causing flow maldistribution. The results are discussed to guide further technological development of this approach to heat exchanger design and fabrication and lays the groundwork for an advanced discretized modeling.
Keywords
heat exchanger; laser welding; microchannel; optimization;
See Also
- Expanded microchannel heat exchanger
- Towards Low-Cost Microchannel Heat Exchangers: Vehicle Heat Recovery Ventilator Prototype
- Open source laser system for polymeric welding
- Laser welding protocol: MOST
- Open Source Multi-Head 3D Printer for Polymer-Metal Composite Component Manufacturing
- Finite Difference Heat Exchanger Model: Flow Maldistribution with Thermal Coupling
Manufacturing the HX with an open source laser welding system
- Experimental Characterization of Heat Transfer in an Additively Manufactured Polymer Heat Exchanger
- Expanded microchannel heat exchanger
- Finite Difference Heat Exchanger Model: Flow Maldistribution with Thermal Coupling
- Open-source laser system for polymeric welding - open source hardware design
- Laser welding protocol: MOST - operating instructions
- Open Source Laser Polymer Welding System: Design and Characterization of Linear Low-Density Polyethylene Multilayer Welds
- Design Optimization of Polymer Heat Exchanger for Automated Household-Scale Solar Water Pasteurizer





