J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MOST}} | {{MOST}} | ||
[[ | ==Source== | ||
*M.P. Brennan, A.L. Abramase, R.W. Andrews, [[J. M. Pearce]], [http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2014.01.046 Effects of spectral albedo on solar photovoltaic devices], ''Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells'', 124, pp. 111-116,(2014). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2014.01.046. [https://www.academia.edu/6222506/Effects_of_spectral_albedo_on_solar_photovoltaic_devices open access] | |||
==See | ==Abstract== | ||
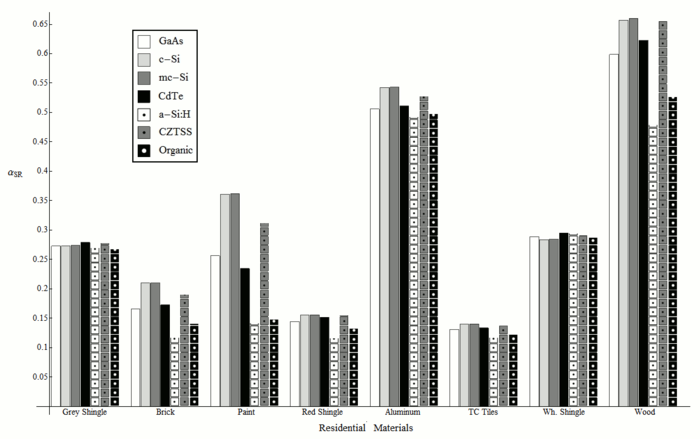
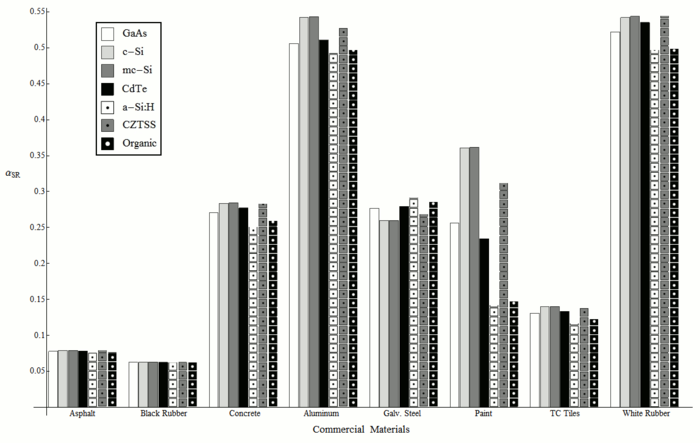
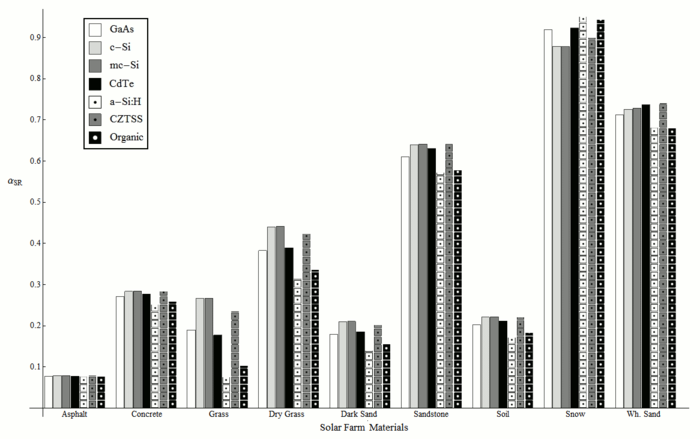
Although the spectral effects of direct and diffuse radiation on [[solar photovoltaic]] (PV) performance are relatively well understood, recent investigations have shown that there can be a spectral bias introduced due to albedo from common ground surfaces that can impact the optimal selection of PV materials for a known location. This paper extends analysis to the effects of spectral bias due to the specular reflectivity of 22 commonly occurring surface materials (both man-made and natural) and analyzes the albedo effects on the performance of seven PV materials covering three common PV system topologies: industrial (solar farms), commercial flat rooftops and residential pitched roof applications. An effective albedo is found for each surface material and PV material combination, which can be used in lieu of broadband albedo values in PV simulations. These results enable PV material selection for specific environments enabling geographic optimization for the micro-environment, while at the same time assisting optimal surface selection in the vicinity of existing or planned PV arrays. This analysis is of particular significance for the modeling of performance of bi-facial PV modules and vertical [[BIPV]]. | |||
==Highlights== | |||
* Spectral bias from ground albedo impacts optimal selection of photovoltaic materials. | |||
* Analyzed specular reflectivity of 22 commonly occurring surface materials. | |||
* Determined albedo effects on the performance of seven PV materials. | |||
* Investigated solar farms, commercial flat rooftops and residential pitched roofs. | |||
* Results enable PV selection for environments enabling geographic optimization. | |||
==Major Findings== | |||
[[image:Residentialroofalbedo.png|700px]] | |||
[[image: Commercialroofalbedo.png|700px]] | |||
[[image:Solarfarmalbedo.png|700px]] | |||
==See Also== | |||
* [[The effect of spectral albedo on amorphous silicon and crystalline silicon solar photovoltaic device performance]] | |||
* [[Solar_resource_measurement_for_PV_applications]] | * [[Solar_resource_measurement_for_PV_applications]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Solar resource measurement for PV applications]] | ||
* [[Atmospheric radiation transfer for PV applications]] | |||
* [[Spectral effects on amorphous silicon photovoltaic cells literature review]] | |||
* [[Design of Multi-Junction Photovoltaic Cells Optimized for Varied Atmospheric Conditions]] | |||
* [[SBDART protocol: MOST]] | |||
* [[Remote spectral prediction for PV applications]] | |||
* [[SEARC spectral project]] | |||
{{Solar navbox}} | |||
[[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | |||
[[Category:Photovoltaics]] | |||
[[category: QAS completed projects and publications]] | |||
Revision as of 23:06, 24 October 2014
Source
- M.P. Brennan, A.L. Abramase, R.W. Andrews, J. M. Pearce, Effects of spectral albedo on solar photovoltaic devices, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 124, pp. 111-116,(2014). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2014.01.046. open access
Abstract
Although the spectral effects of direct and diffuse radiation on solar photovoltaic (PV) performance are relatively well understood, recent investigations have shown that there can be a spectral bias introduced due to albedo from common ground surfaces that can impact the optimal selection of PV materials for a known location. This paper extends analysis to the effects of spectral bias due to the specular reflectivity of 22 commonly occurring surface materials (both man-made and natural) and analyzes the albedo effects on the performance of seven PV materials covering three common PV system topologies: industrial (solar farms), commercial flat rooftops and residential pitched roof applications. An effective albedo is found for each surface material and PV material combination, which can be used in lieu of broadband albedo values in PV simulations. These results enable PV material selection for specific environments enabling geographic optimization for the micro-environment, while at the same time assisting optimal surface selection in the vicinity of existing or planned PV arrays. This analysis is of particular significance for the modeling of performance of bi-facial PV modules and vertical BIPV.
Highlights
- Spectral bias from ground albedo impacts optimal selection of photovoltaic materials.
- Analyzed specular reflectivity of 22 commonly occurring surface materials.
- Determined albedo effects on the performance of seven PV materials.
- Investigated solar farms, commercial flat rooftops and residential pitched roofs.
- Results enable PV selection for environments enabling geographic optimization.
Major Findings
See Also
- The effect of spectral albedo on amorphous silicon and crystalline silicon solar photovoltaic device performance
- Solar_resource_measurement_for_PV_applications
- Solar resource measurement for PV applications
- Atmospheric radiation transfer for PV applications
- Spectral effects on amorphous silicon photovoltaic cells literature review
- Design of Multi-Junction Photovoltaic Cells Optimized for Varied Atmospheric Conditions
- SBDART protocol: MOST
- Remote spectral prediction for PV applications
- SEARC spectral project