J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) m (→See Also) |
Sophivorus (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[image:" to "[[Image:") |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Ito-gas.gif|thumb]] | |||
{{MOST}} | {{MOST}} | ||
{{Source data | |||
= | | type = Paper | ||
Marikkannan, M. and Subramanian, M. and Mayandi, J. and Tanemura, M. and Vishnukanthan, V. and Pearce, J. M., [http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/adva/5/1/10.1063/1.4906566 Effect of ambient combinations of argon, oxygen, and hydrogen on the properties of DC magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide films], ''AIP Advances'', '''5''', 017128 (2015), DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4906566 [https://www.academia.edu/10297219/Effect_of_ambient_combinations_of_argon_oxygen_and_hydrogen_on_the_properties_of_DC_magnetron_sputtered_indium_tin_oxide_films open access] | | cite-as = Marikkannan, M. and Subramanian, M. and Mayandi, J. and Tanemura, M. and Vishnukanthan, V. and Pearce, J. M., [http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/adva/5/1/10.1063/1.4906566 Effect of ambient combinations of argon, oxygen, and hydrogen on the properties of DC magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide films], ''AIP Advances'', '''5''', 017128 (2015), DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4906566 [https://www.academia.edu/10297219/Effect_of_ambient_combinations_of_argon_oxygen_and_hydrogen_on_the_properties_of_DC_magnetron_sputtered_indium_tin_oxide_films open access] | ||
}} | |||
Sputtering has been well-developed industrially with singular ambient gases including neutral argon (Ar), oxygen (O<sub>2</sub>), hydrogen (H<sub>2</sub>) and nitrogen (N<sub>2</sub>) to enhance the electrical and optical performances of indium tin oxide (ITO) films. Recent preliminary investigation into the use of combined ambient gases such as an Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub> ambient mixture, which was suitable for producing high-quality (low sheet resistance and high optical transmittance) of ITO films. To build on this promising preliminary work and develop deeper insight into the effect of ambient atmospheres on ITO film growth, this study provides a more detailed investigation of the effects of ambient combinations of Ar, O<sub>2</sub>, H<sub>2</sub> on sputtered ITO films. Thin films of ITO were deposited on glass substrates by DC magnetron sputtering using three different ambient combinations: Ar, Ar+O<sub>2</sub> and Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub>. The structural, electrical and optical properties of the three ambient sputtered ITO films were systematically characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman spectroscopy, four probe electrical conductivity and optical spectroscopy. The XRD and Raman studies confirmed the cubic indium oxide structure, which is polycrystalline at room temperature for all the samples. AFM shows the minimum surface roughness of 2.7 nm for Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub> sputtered thin film material. The thickness of the films was determined by the cross sectional SEM analysis and its thickness was varied from 920 to 817 nm. The columnar growth of ITO films was also discussed here. The electrical and optical measurements of Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub> ambient combinations shows a decreased sheet resistance (5.06 ohm/□) and increased optical transmittance (69%) than other samples. The refractive index and packing density of the films were projected using optical transmission spectrum. From the observed results the Ar+O2+H2 ambient is a good choice to enhance the total optoelectronic properties of the ITO films. The improved electrical and optical properties of ITO films with respect to the Ar+O2+H2 ambient sample were discussed in detail. In addition, the physical properties were also discussed with the influence of this ambient combination with respect to Ar, Ar+O<sub>2</sub> and Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub>. | Sputtering has been well-developed industrially with singular ambient gases including neutral argon (Ar), oxygen (O<sub>2</sub>), hydrogen (H<sub>2</sub>) and nitrogen (N<sub>2</sub>) to enhance the electrical and optical performances of indium tin oxide (ITO) films. Recent preliminary investigation into the use of combined ambient gases such as an Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub> ambient mixture, which was suitable for producing high-quality (low sheet resistance and high optical transmittance) of ITO films. To build on this promising preliminary work and develop deeper insight into the effect of ambient atmospheres on ITO film growth, this study provides a more detailed investigation of the effects of ambient combinations of Ar, O<sub>2</sub>, H<sub>2</sub> on sputtered ITO films. Thin films of ITO were deposited on glass substrates by DC magnetron sputtering using three different ambient combinations: Ar, Ar+O<sub>2</sub> and Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub>. The structural, electrical and optical properties of the three ambient sputtered ITO films were systematically characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman spectroscopy, four probe electrical conductivity and optical spectroscopy. The XRD and Raman studies confirmed the cubic indium oxide structure, which is polycrystalline at room temperature for all the samples. AFM shows the minimum surface roughness of 2.7 nm for Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub> sputtered thin film material. The thickness of the films was determined by the cross sectional SEM analysis and its thickness was varied from 920 to 817 nm. The columnar growth of ITO films was also discussed here. The electrical and optical measurements of Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub> ambient combinations shows a decreased sheet resistance (5.06 ohm/□) and increased optical transmittance (69%) than other samples. The refractive index and packing density of the films were projected using optical transmission spectrum. From the observed results the Ar+O2+H2 ambient is a good choice to enhance the total optoelectronic properties of the ITO films. The improved electrical and optical properties of ITO films with respect to the Ar+O2+H2 ambient sample were discussed in detail. In addition, the physical properties were also discussed with the influence of this ambient combination with respect to Ar, Ar+O<sub>2</sub> and Ar+O<sub>2</sub>+H<sub>2</sub>. | ||
==See | {{Pearce publications notice}} | ||
*[[Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | |||
*[[Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices]] | == See also == | ||
*[[Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | |||
*[[Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review]] | * [[Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | ||
*[[Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation]] | * [[Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices]] | ||
* [[Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | |||
* [[Influence of Oxygen Concentration on the Performance of Ultra-Thin RF Magnetron Sputter Deposited Indium Tin Oxide Films as a Top Electrode for Photovoltaic Devices]] | |||
* [[Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review]] | |||
* [[Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation]] | |||
* [[A new method of preparing highly conductive ultra-thin indium tin oxide for plasmonic-enhanced thin film solar photovoltaic devices]] | |||
* [[Ambiance-dependent Agglomeration and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Response of Self-assembled Silver Nano-particles for Plasmonic Photovoltaic Devices]] | |||
* [[Micromorphology analysis of sputtered indium tin oxide fabricated with variable ambient combinations]] | |||
* [[Scalable honeycomb top contact to increase the light absorption and reduce the series resistance of thin film solar cells]] | |||
{{Page data | |||
| title-tag = Effect of Gas Mixtures on ITO Films | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | [[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:09, 16 April 2024
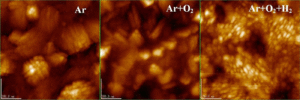
Sputtering has been well-developed industrially with singular ambient gases including neutral argon (Ar), oxygen (O2), hydrogen (H2) and nitrogen (N2) to enhance the electrical and optical performances of indium tin oxide (ITO) films. Recent preliminary investigation into the use of combined ambient gases such as an Ar+O2+H2 ambient mixture, which was suitable for producing high-quality (low sheet resistance and high optical transmittance) of ITO films. To build on this promising preliminary work and develop deeper insight into the effect of ambient atmospheres on ITO film growth, this study provides a more detailed investigation of the effects of ambient combinations of Ar, O2, H2 on sputtered ITO films. Thin films of ITO were deposited on glass substrates by DC magnetron sputtering using three different ambient combinations: Ar, Ar+O2 and Ar+O2+H2. The structural, electrical and optical properties of the three ambient sputtered ITO films were systematically characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman spectroscopy, four probe electrical conductivity and optical spectroscopy. The XRD and Raman studies confirmed the cubic indium oxide structure, which is polycrystalline at room temperature for all the samples. AFM shows the minimum surface roughness of 2.7 nm for Ar+O2+H2 sputtered thin film material. The thickness of the films was determined by the cross sectional SEM analysis and its thickness was varied from 920 to 817 nm. The columnar growth of ITO films was also discussed here. The electrical and optical measurements of Ar+O2+H2 ambient combinations shows a decreased sheet resistance (5.06 ohm/□) and increased optical transmittance (69%) than other samples. The refractive index and packing density of the films were projected using optical transmission spectrum. From the observed results the Ar+O2+H2 ambient is a good choice to enhance the total optoelectronic properties of the ITO films. The improved electrical and optical properties of ITO films with respect to the Ar+O2+H2 ambient sample were discussed in detail. In addition, the physical properties were also discussed with the influence of this ambient combination with respect to Ar, Ar+O2 and Ar+O2+H2.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices
- Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Influence of Oxygen Concentration on the Performance of Ultra-Thin RF Magnetron Sputter Deposited Indium Tin Oxide Films as a Top Electrode for Photovoltaic Devices
- Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review
- Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation
- A new method of preparing highly conductive ultra-thin indium tin oxide for plasmonic-enhanced thin film solar photovoltaic devices
- Ambiance-dependent Agglomeration and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Response of Self-assembled Silver Nano-particles for Plasmonic Photovoltaic Devices
- Micromorphology analysis of sputtered indium tin oxide fabricated with variable ambient combinations
- Scalable honeycomb top contact to increase the light absorption and reduce the series resistance of thin film solar cells





