(Created page with "thumb|right|200px|Hydrogen made from waste plant parts '''Biohydrogen''' is hydrogen produced trough a [[biological processes|biologi...") Tag: n |
No edit summary Tag: n |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Microbial_electrolysis_cell.png|thumb|right|200px|Hydrogen made from waste plant parts]] | [[File:Microbial_electrolysis_cell.png|thumb|right|200px|Hydrogen made from waste plant parts]] | ||
'''Biohydrogen''' is [[hydrogen]] produced trough a [[biological processes|biological process]], most commonly by [[algae]], [[bacteria]] or archaea. The [[biofuel]] is producable from waste organic materials.<ref>Demirbas, A. (2009). Biohydrogen: For Future Engine Fuel Demands. Trabzon: Springer. ISBN 1-84882-510-2</ref> | '''Biohydrogen''' is [[hydrogen]] produced trough a [[biological processes|biological process]], most commonly by [[algae]], [[bacteria]] or archaea. The [[biofuel]] is producable from waste organic materials.<ref>Demirbas, A. (2009). Biohydrogen: For Future Engine Fuel Demands. Trabzon: Springer. ISBN 1-84882-510-2</ref><ref>[http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/03/090330111257.htm Biohydrogen can also be converted to methane to eliminate the gas storage problems of pure hydrogen]</ref> | ||
==References== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
[[Category:Energy production]] | [[Category:Energy production]] | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 28 July 2012
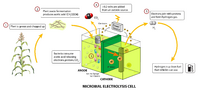
Biohydrogen is hydrogen produced trough a biological process, most commonly by algae, bacteria or archaea. The biofuel is producable from waste organic materials.[1][2]
References
- ↑ Demirbas, A. (2009). Biohydrogen: For Future Engine Fuel Demands. Trabzon: Springer. ISBN 1-84882-510-2
- ↑ Biohydrogen can also be converted to methane to eliminate the gas storage problems of pure hydrogen