| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Methodology== | ==Methodology== | ||
The methodology is divided into three parts: (1) pre-simulation, (2) simulation and | |||
(3) post-simulation. Pre-simulation details data input acquisition and manipulation to meet r.sun's | |||
parameters, which were often lightly treated, but are often the most time consuming and challenging | |||
part of any GIS related project. Therefore pre-simulation steps will be presented here in a transparent | |||
fashion to ease the work of upcoming PV deployment projects and to make the methodology as omniapplicable | |||
as possible. Simulation is the running of the package itself. Post-simulation will include | |||
calculating of an annual yields based on monthly estimates and optimal siting for candidate solar | |||
parks/farms. Due to the complex nature of modeling radiation and the relatively unfamiliarity of the | |||
scientific community outside Europe with r.sun to ensure precision many steps were carried out on the proprietary ArcMap software version 9.3. However, the GRASS counterpart for a step is included in order to allow for greater access. | |||
The required data inputs include: | |||
- Census Subdivisions (CSD) of the 14 counties in the RER | |||
- Soil types for forestry | |||
- Soil types for agriculture | |||
- Land use classification (exclusive of agriculture) | |||
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM) | |||
- Slope/ inclination: the angle between the plane of the surface in question and the equator plane | |||
- Aspect/ orientation: the surface azimuth angle, the deviation of the projection of the normal to the | |||
plane in question on the equator plane from the local meridian | |||
- Latitude: the angular location north or south of the equator‟s plane | |||
- Albedo: the ratio of diffusely reflected radiation on a surface to its incident radiation | |||
- Mean days and corresponding angular position of the sun | |||
- Linke turbidity: a convenient approximation to model the atmospheric absorption and scattering | |||
of the solar radiation under clear skies | |||
- Ground-measured values of global horizontal irradiation (GHI) | |||
- Clear sky index Kc: ratio of the global horizontal irradiance to the global horizontal irradiance | |||
under clear sky conditions6. It is important not to confuse and hence misuse this definition with | |||
those for insolation clearness index and clear sky insolation clearness index | |||
==Result== | ==Result== | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 26 August 2010
Introduction
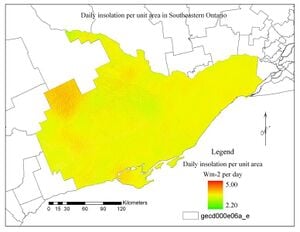
This is an investigation of the capacity and capabilities of the module r.sun, one of the utilities of the Geographical Resources Analysis Support System (GRASS). Using Southeastern Ontario as case study, insolation, including temporal and spatial variation of albedo, was computed to output reliable solar energy for large scale solar PV farm development in the region.
Background
A comprehensive background for modeling solar energy can be found in Duffie J.A. and W.A. Beckman. (1991). Solar Engineering of Thermal processes. John Wiley & Sons, 2ed.
Hofierka J., Šúri M. (2002). The solar radiation model for Open source GIS: implementation and applications. Proceedings of the Open source GIS - GRASS users conference, Italy. provides a detailed guide on how to run the module.
Methodology
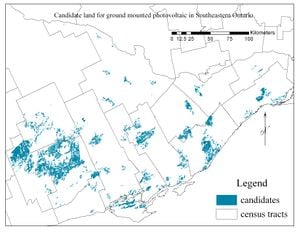
The methodology is divided into three parts: (1) pre-simulation, (2) simulation and (3) post-simulation. Pre-simulation details data input acquisition and manipulation to meet r.sun's parameters, which were often lightly treated, but are often the most time consuming and challenging part of any GIS related project. Therefore pre-simulation steps will be presented here in a transparent fashion to ease the work of upcoming PV deployment projects and to make the methodology as omniapplicable as possible. Simulation is the running of the package itself. Post-simulation will include calculating of an annual yields based on monthly estimates and optimal siting for candidate solar parks/farms. Due to the complex nature of modeling radiation and the relatively unfamiliarity of the scientific community outside Europe with r.sun to ensure precision many steps were carried out on the proprietary ArcMap software version 9.3. However, the GRASS counterpart for a step is included in order to allow for greater access.
The required data inputs include: - Census Subdivisions (CSD) of the 14 counties in the RER - Soil types for forestry - Soil types for agriculture - Land use classification (exclusive of agriculture) - Digital Elevation Model (DEM) - Slope/ inclination: the angle between the plane of the surface in question and the equator plane - Aspect/ orientation: the surface azimuth angle, the deviation of the projection of the normal to the plane in question on the equator plane from the local meridian - Latitude: the angular location north or south of the equator‟s plane - Albedo: the ratio of diffusely reflected radiation on a surface to its incident radiation - Mean days and corresponding angular position of the sun - Linke turbidity: a convenient approximation to model the atmospheric absorption and scattering of the solar radiation under clear skies - Ground-measured values of global horizontal irradiation (GHI) - Clear sky index Kc: ratio of the global horizontal irradiance to the global horizontal irradiance under clear sky conditions6. It is important not to confuse and hence misuse this definition with those for insolation clearness index and clear sky insolation clearness index
Result