(adding images/) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
# Woodlot - Stamd trees in a seperate area for use | # Woodlot - Stamd trees in a seperate area for use | ||
# Windbreak | # Windbreak | ||
[[windbreak.gif |none|thumb|Windbreaks]] | [[Image:windbreak.gif |none|thumb|Windbreaks]] | ||
# Live fencing | # Live fencing | ||
# Compound trees - Fruit, ornamental, shade | # Compound trees - Fruit, ornamental, shade | ||
# Buffer zone - To stop attack of crops by pests | # Buffer zone - To stop attack of crops by pests | ||
# Alley cropping - On plains, plateaus | # Alley cropping - On plains, plateaus | ||
[[alleycropping.gif |none|thumb|Alley cropping]] | [[Image:alleycropping.gif |none|thumb|Alley cropping]] | ||
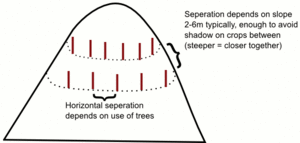
# Contour planting - On steep gradients stops erosion | # Contour planting - On steep gradients stops erosion | ||
[[contourplanting.gif |none|thumb|Using contour plating]] | [[Image:contourplanting.gif |none|thumb|Using contour plating]] | ||
[[Category:Food_and_Agriculture]] | [[Category:Food_and_Agriculture]] | ||
Revision as of 20:26, 29 April 2007
Introduction
Agroforestry is a land use system in which trees and/or shrubs are managed with crops and/or livestock on the same piece of land (although not necessarily at the same time).
Agroforestry can have positive economic effects through better utilisation of land, and also environmentally as the different types of crop on the land work together and compliment each other.
Use of trees in agroforestry
- Enhancing soil fertility
- Through leaf fall
- Roots add nitrogen to soil through nodules in the roots (bacteria fixes nirogen -> nitrates)
- Recycling nutrients - Deep roots take nutrients from deep in soil and pass closer to surface. Useful if soil has been leached
- Nitrogen fixing trees - Compound leaves, flowers in pods, nodules (e.g calliandra, sespania, machuna, lusena, albizia, casuaniara, tithonia)
- Controlling soil erosion
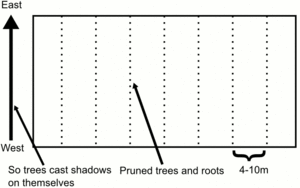
- Acting as a wind break
- Wind at start of the rainy season can destroy crops
- Need trees with strong deep roots (e.g. mangos, jack fruit, musambia, mysopsis)
- Use as supporting poles in building
- Live Fencing
- (e.g Lantana camara [aka Kapange], Kei apple trees, Cyprus [aka xmas tree], Ficus, Kilowa, Glyricidia, Bustani, Caliandra)
- Fruits, Fodder, Medicine, Fuel
- Medicinal trees - Moringa, neem, melia
- Fodder trees - calliandra (high protein content), lucana, glyvidia, titonia (for goats), ficus, avocado - Using these as a live fence and then pruning a section for fodder each day/week is a useful method for controlled live fences and regular fodder
- Trees help in supression of weeds
Managing agroforestry trees
Trees require water, air, light, materials - Hence potential competition (particularly when intercropping)
- Pruning - Also produces fodder. Trees regenerate and you can cut all the crown without killing the tree
- Lopping - Removing end of branches, reduces shadow
- Spacing of trees - (e.g mango - 12m)
- Prune the roots - (e.g calliandria - dig 1ft with hoe and cut the roots every season -> keeps nutrients at top of soil, encourages deep root growth)
Types of agroforestry arrangements
- Boundary planting
- Scattered within crops
- Woodlot - Stamd trees in a seperate area for use
- Windbreak

- Live fencing
- Compound trees - Fruit, ornamental, shade
- Buffer zone - To stop attack of crops by pests
- Alley cropping - On plains, plateaus
- Contour planting - On steep gradients stops erosion