CHAPTER V. ORGANISATION OF PRODUCTION AND INFRASTRUCTURAL REQUIREMENTS[edit | edit source]
The efficient organisation of production and the availability of an adequate infrastructure constitute important requirements for the good running of merchant mills which, in addition to milling the grain, need to store the raw materials and the output, package the meal, etc. Furthermore, depending on circumstances, small- to medium-scale merchant mills may also need to shell and clean the maize grain, and undertake some limited sifting of the whole meal for the removal of large pieces of bran and germ.
The above requirements are much more stringent in the case of large-scale roller mills which require, in addition, an efficient management of the plant. On the other hand, small custom mills, which only process shelled maize brought by customers, require a simple infrastructure and little management.
Since this memorandum is mostly concerned with the promotion of custom and small-scale merchant mills, this chapter will focus on the organisation of production, and the infrastructural and managerial requirements of the above mills.
I. SKILL REQUIREMENTS[edit | edit source]
The running of milling equipment requires skills which may be acquired in a relatively short time through, for example, on-the-job training. The mill operators need only know how to adjust the mill for the production of various types of meal and the processing of various types of grain. On the other hand, the repair and maintenance of the equipment require mechanical skills and, in some cases, a minimal knowledge of electricity. Skills are required for the replacement of defective parts, the re-conditioning of hammers and millstones, the maintenance of electric or petrol engines, etc. Furthermore, improvements of the mill efficiency may require the design and manufacture of simple ancillary equipment.
The above maintenance, repairs or improvements require labour trained in technical schools or training centres. Additional on-the-job training in various mills may also be necessary.
The owners of custom mills should be responsible for all maintenance and repair activities since it would be too costly to hire skilled labour for this purpose. On the other hand, merchant mills may benefit from the full-time use of a skilled repair and maintenance operative, especially if the owner must handle managerial and supervisory tasks, as well as the buying of grains and the marketing of the output.
II. INFRASTRUCTURAL REQUIREMENTS[edit | edit source]
Infrastructural requirements depend on the type and capacity of the mill as well as on the need to store the raw materials and/or output. They also depend on whether the mill carries out pre-milling (e.g. shelling, cleaning) and/or post-milling (e.g. sifting, packaging) operations.
Depending on the adopted engine, mills may require an electric supply line or a petrol/diesel storage area. In areas where the supply of electricity is not dependable, mill owners should consider the use of petrol or diesel engines if they wish to avoid costly shutdowns of the mill. If electric power is much less expensive than other sources of energy, mill owners should assess the feasibility of investing in an electricity generator to compensate for electricity failures.
The buildings in which the milling equipment is installed and the storage areas should be well ventilated since the milling process generates a large amount of dust. The buildings should also be provided with a good lighting system in case the mill is operated on a two-shift basis.
Adequate roofing material should be used in order to avoid damage of the grain or whole meal by rainwater. The floor of the buildings should preferably be cemented to minimise the contamination of the whole meal by sand or dirt and to facilite the cleaning of the floor.
Space requirements
The space requirements for various types of mills and scales of production depend on the number of operations carried out by the mill (e.g. shelling, milling, sifting, bagging), the need for storing the raw material and/or output, the selected source of energy, etc. Thus, the space requirement for a given mill may not be estimated without detailed information on the characteristics and design of the mill. Consequently, this memorandum provides only indicative figures of space requirements rather than precise estimates of the latter for each type of mill.
The space requirement and a basic layout of six types of small-scale mills are provided in this section. The output of these mills varies from 1 to 8 tonnes per 8-hour working day. Table V.1 indicates the space requirements for each operation and storage area, for offices, etc. Pre- and post-milling operations, such as shelling, drying and sifting are not included. Additional space for these operations must be estimated if it is intended to carry out some or all of these operations.
Storage areas are calculated on the basis of 2 m3 per tonne of grain in bags and 1 m3 per tonne of whole meal. Grain stored in bulk requires less space, approximately 1.5 to 1.7 m3 per tonne of grain. A requirement of six days' storage is assumed. Larger or smaller storage capacities may be required according to specific local conditions.
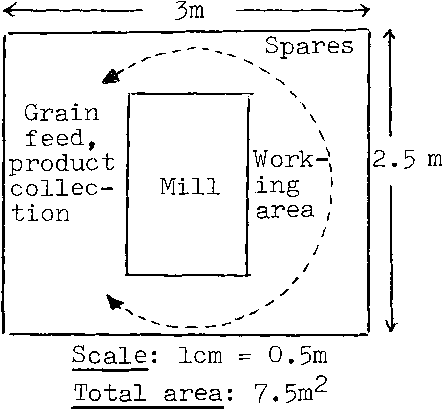
Figure V.1 illustrates the layout of an electricity-powered, horizontal stone mill with a capacity of 2 tonnes of maize per 8 hours (mill No. 2 in table V.1). It is intended to be a custom mill with no storage facilities since customers bring in grain and leave with whole meal.
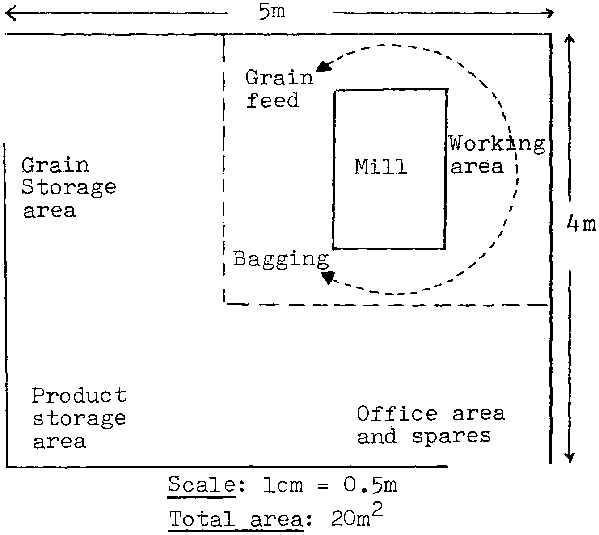
Figure V.2 shows the layout of a similar mill which operates as a small-scale merchant mill as well as a custom mill (mill No. 3 in table V.1). In this case, the floor area is larger as both grain storage and product storage areas are needed.
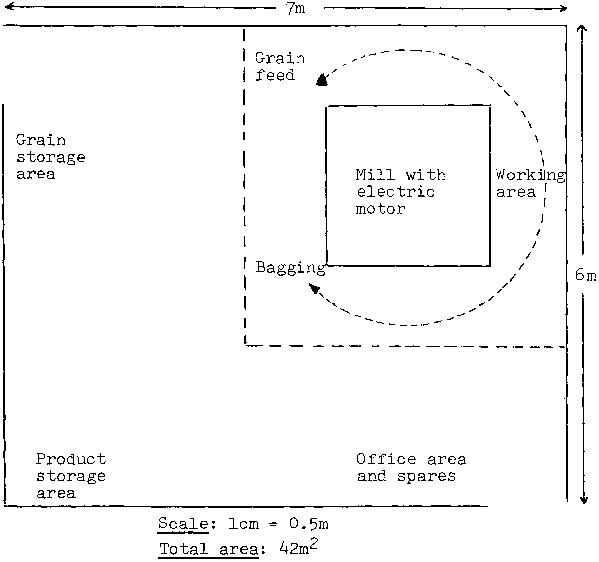
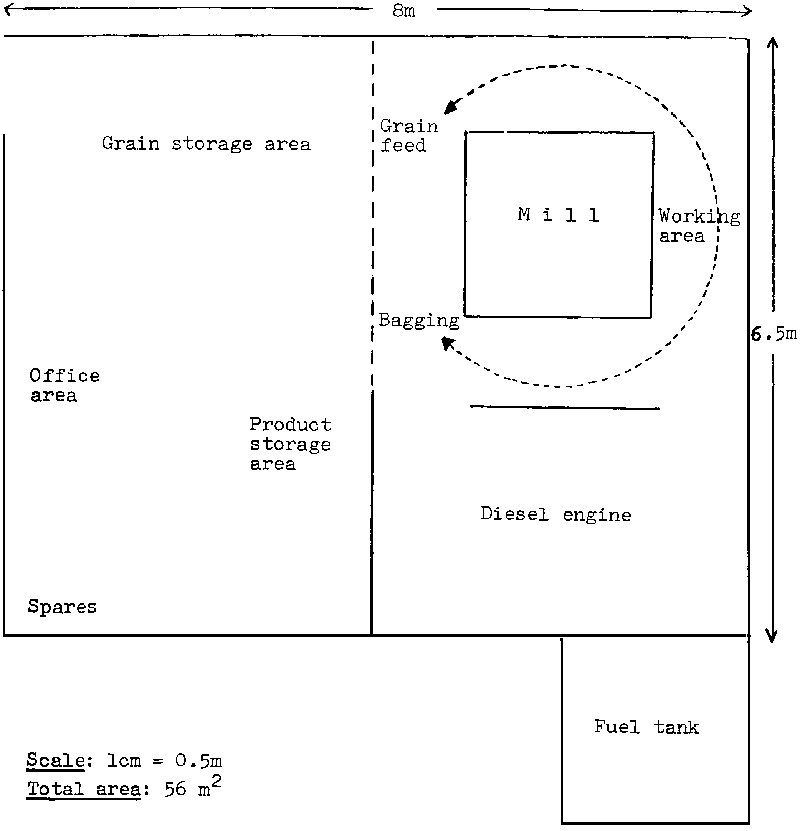
Figure V.3 illustrates the layout of an electricity-powered hammer mill with a capacity of 4 tonnes of grain per 8-hour day (mill No. 5 in table V.1). This type of mill requires sufficiently large grain storage and product storage areas, as well as space for bagging/packaging and for an office. A mill with the same capacity, but powered by a diesel engine, requires additional space for the engine and a fuel tank (see figure V.4).
The layout of the other plants included in table V.1 are similar to those shown in figures V.1 to V.4.
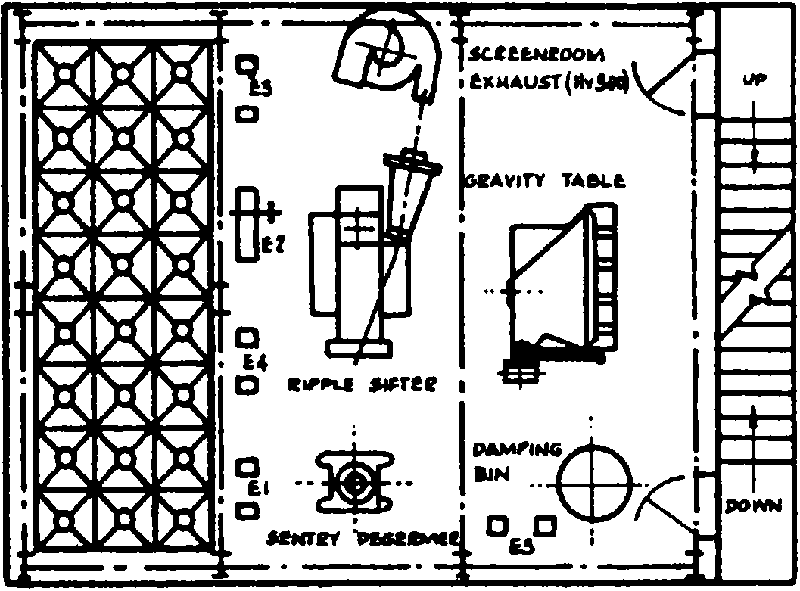
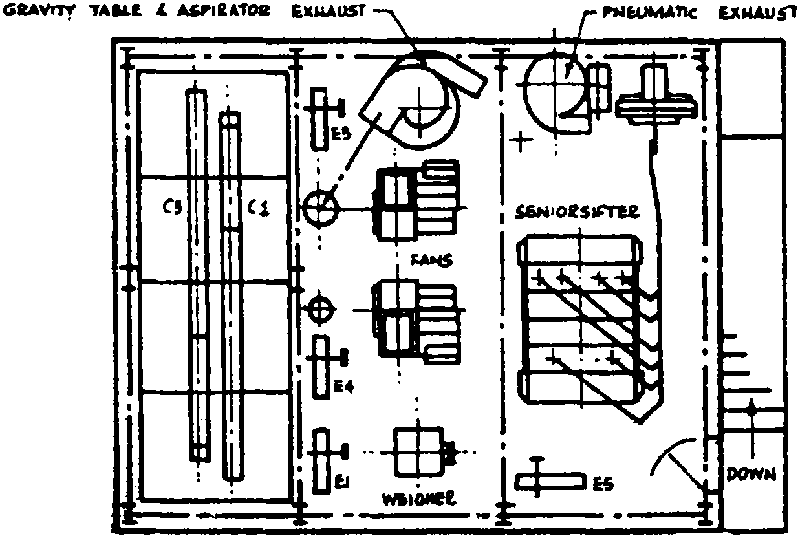
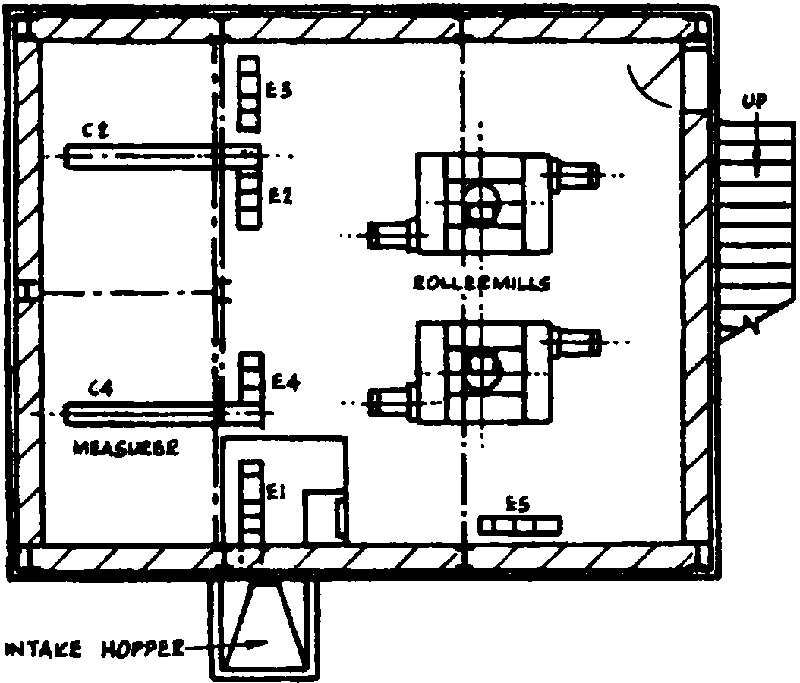
Modern roller mills require a larger infrastructure. The factory layout is of paramount importance to ensure a maximum space utilisation. Figure V.5 illustrates the layout of a three-storey, specially designed roller mill with a capacity of 2 tonnes per hour (the material is gravity-fed from one operation to the next). However, a single storey building of larger floor area could be used if it is sufficiently high for the elevation of the materials through the various milling stages.
Suggested space requirements for various types of small-scale mills
|
Floor space (m2) | |||||||
|
Mill number |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 | |
|
Type* |
P |
S(h) |
S(h) |
H |
H |
H | |
|
Capacity of mill (tonnes/8 hr) |
1 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
4 |
8 | |
|
Mill with electric motor |
1 |
|
|
4 |
4 |
9 | |
|
Grain feed in |
1 |
|
|
2 |
2 |
4 | |
|
Product bagging/packing |
1 |
|
|
2 |
4 |
6 | |
|
Grain storage |
|
12 |
24 | ||||
|
Product storage |
|
6 |
12 | ||||
|
Work space, including maintenance |
2 |
|
|
4 |
7 |
7 | |
|
Spares |
1 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
2 | |
|
Office |
|
6 |
6 | ||||
|
Diesel engine room |
10 |
10 |
12 | ||||
|
10. |
Fuel tanks |
4 |
4 |
4 | |||
|
11. |
Total with electric motor |
6 |
|
20.0 |
13 |
42 |
70 |
|
12. |
Total with diesel engine |
27 |
56 |
86 | |||
* P: Plate mill
S: Stone mill
(h): Horizontal
H: Hammer mill
Figure V.1 Custom-operated, electricity-powered horizontal stone mill - 2 tonnes maize per 8 hours
Figure V.2 Commercially-operated, electricity-powered horizontal stone mill, 2 tonnes maize per 8 hours
Figure V.3 Commercially-operated, electricity-powered hammer mill - 4 tonnes maize per 8 hours
Figure V.4 Commercially-operated, diesel-powered hammer mill - 4 tonnes maize per 8 hours
Figure V.5
Floor plan of a three-storey roller mill - 2 tonnes maize per hour
1st FLOOR PLAN
2nd FLOOR PLAN
GROUND FLOOR PLAN