
AI stands for Artificial Intelligence and its an interdisciplinary branch of computer science with the intention to reproduce certain abstract calculable aspects of human insight and thought processes onto computers and to offer solutions with the help of computers to problems that require intelligent performance. This is indispensable in our mordern world but it also brings some disadvantages. AI is marked interdisciplinarily by computer science, mathematics, cognitive psychology, neuroscience, linguistics and philosophy. Many parts of AI works hand in hand with robotics.
Subjects[edit | edit source]
Chronology[edit | edit source]
Past[edit | edit source]
In the past humans have done all the hard work, like putting together a car or moving heavy materials from one place to another, themselves. But as our technology got better we've been able to get robots to do these hard and tedious tasks for us, thanks to artificial intelligence.
Present[edit | edit source]
Today we have still machines who have to be controlled manually by humans but we also have more and more machines who can act autonomous. Some machines with AI just do simple translations by using human created libraries. But today we have also very intelligent AI with the autonoumous self driving prototype of the "Google Driverless Car".
Future[edit | edit source]
Nobody knows what the future will bring but we see clear trends.
- Self driving cars
- Human robots
- Autonomous military robots and AI software (look also: Military)
- Replacing human's work
- Human extinction?
Long Term Goals[edit | edit source]
Philosophy[edit | edit source]
- Can a machine act intelligently? Can it solve any problem that a person would solve by thinking?
- Are human intelligence and machine intelligence the same? Is the human brain essentially a computer?
- Can a machine have a mind, mental states and consciousness in the same sense humans do? Can it feel how things are?
AI vs mankind[edit | edit source]
- The beginning of the end for humanity?
Tools[edit | edit source]
Search[edit | edit source]
The AI is concerned with subject like search algorithms. Different search algorithms can be used. Important algorithms are those for pathfinding. Pathfinding describes a searching process for optimal paths.
Planning[edit | edit source]
Planning is an important point of the AI. The process of planning is divided into two phases:
- aim formulation: Defining an aim.
- problem formulation: Which actions and world conditions should be treated.
Machine learning[edit | edit source]
Machine learning is a big subject of artificial intelligence. The subject contains algorithms that improves automatically through experience. Another definition is the artificial generation of knowledge through experience.
Algorithms[edit | edit source]
- supervised learning
- unsupervised learning
- reinforcement learning
Algorithms[edit | edit source]
Evolutionary algorithms[edit | edit source]
Applications[edit | edit source]
Chess computer[edit | edit source]
- Deep Blue, a chess-playing computer developed by IBM which beat Garry Kasparov in 1997.
IBM Watson[edit | edit source]

A pilot service by IBM to uncover and share data-driven insights, and to spur cognitive applications. A question answering system developed by IBM to play the Jeopardy! game show.
Description[edit | edit source]
Watson is a question answering (QA) computing system that IBM built to apply advanced natural language processing, information retrieval, knowledge representation, automated reasoning, and machine learning technologies to the field of open domain question answering.
Software[edit | edit source]
Watson uses IBM's DeepQA software and the Apache UIMA (Unstructured Information Management Architecture) framework. The system was written in various languages, including Java, C++, and Prolog, and runs on the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 operating system using Apache Hadoop framework to provide distributed computing.
Hardware[edit | edit source]
Watson is composed of a cluster of ninety IBM Power 750 servers, each of which uses a 3.5 GHz POWER7 eight core processor, with four threads per core. In total, the system has 2,880 POWER7 processor cores and has 16 terabytes of RAM.
Future Use[edit | edit source]
Autonomous vehicles[edit | edit source]
Autonomous vehicles (driverless car) are vehicles, that are able to navigate, without an human input. They use various sensors (GPS, computer vision)to sense the environment.
Examples[edit | edit source]
- Google Driverless Car
- The car using a 360° laser sensor to scan the area
- It works on the normal streets
Advantages[edit | edit source]
- Less traffic congestion
- Smooth riding
- (Maybe) less number of accidents
- Some jobs can be done more effectivly
- Humans don't need to drive cars through dangerous areas anymore
Disadvantages[edit | edit source]
- Liability for accidents
- Ethical problems: How to react in a potential crash situation
- Loss of some jobs
Robotics[edit | edit source]
Robots with soul[edit | edit source]
Playful, reactive and courious Robots. First attempts were made by creating robots which can interact by spontaneous making music with humans. Less mechanical structure and more gentle and smooth robotic behaviour allows robots to look more friendly. Focusing the development of robots who either work with humans insted of executing simple instructions robots are accepted as an partner. This can be viewed as a robotic revolution because of its more intuitive and risk taking behaviour.
Guy Hoffman´s research in human-robot interaction deals with teamwork and collaboration between the robot and a human. His Shimon-robot is a try to connect human musicians to a robot by combining their skills, but also by gestures and behaviour.
Obviously robots will become more humanoid in future. Another example is the Data robot, a stand-up comedian which is capable to gahter audience feedback and even reacting to it. Interesting is it´s individual and unexpecetd perfomance.
Modern robot technology is also affected by arts, acting and cultures.
Drones (UAV - Unmanned aerial vehicle)[edit | edit source]

An UAV is an air vehicle, that is controlled without a human aboard.Drones can be controlled by a computer or via remote controller. A lot of UAVs are remote controlled, but the research and devolopment of autonomous UAVs is going on. Autonomy is the ability to make own decisions. UAVs are also called UAS (Unmanned aircraft system). A drone can be equipped with cameras, weapons etc..
Technology[edit | edit source]
- sensor (sensor fusion: Information from different sensors)
- path planning
- motion planning
Uses[edit | edit source]
- sports (photography)
- military (UCAV)
- intelligence agency
- police
- search and rescue
- fire detection (forest)
- transport vehicles
- sciences
Development[edit | edit source]
There are many US research- and development programms, to develop military drones (i.e. DARPA). The US-Armee constructes drones that use swarm intelligence. Europe is also in the R&D of military drones (i.e. Dassault Neuron). The devolpment of Micro Aerial Vehical (MAV) is a big subject too. MAVs can be used for monitoring or aimed killing.
Missions[edit | edit source]
- 1999: The Bundeswehr did use CL 289 Drones in Kosovo.
- 2003: Hamas tried to get in possesion of a drone. Three leader of hamaz has been killed by explosives.
- 2009: The taliban leader Baitullah Mehsud was killed by an US-Drone. About 2400 people has beend killed by drones until August 2011. The US base Ramstein in germany has been used to control us killer drones.
- 2012: Abu Jahja el Libi (al-Qaida) has been killed by an US-Drone.
Types[edit | edit source]
- MAV (Micro Air Vehicles)
- UAV (Unmanned Aearial Vehicle)
- UAS (Unmanned Aerial System)
- UCAV (Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle)
- URAV (Unmanned Reconnaissance Aerial Vehicle)
- VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)
Developer[edit | edit source]
- Northrup Grumman
- General Atomics
- EADS
- BAE Systems
- Vestel
- Saab
Examples[edit | edit source]
- Global Hawk / Euro Hawk:
- General Atomics MQ-1 Predator
- AAI Corporation Aerosonde
Humanoid robot[edit | edit source]
- A humanoid robot is mostly designed after the appearance of a human. The idea is to create a robot that can act like a human with all his functions. The AI is an significant part to analyse the information the robot receives for example how to manage stairs. Humanoid robots are also used for research, especially in biomeachnics to study the human body structure and behavior. A yearly event is the RoboCup wich is an robotics competition with the aim to promote robotics and AI research. The main dream of the RoboCup is to create a robot football team capable of beating the human football world champions. The RoboCup also deals with topics like rescue where robots are used for disaster assistance and rescue.
Speech recognition[edit | edit source]
Speech recognitions means the translation of speech into a text (STT = speec to text). Some systems has to be "trained" to understand the individual speaker, called "speaker-dependent" systems and systems without are called "speaker-independent" systems. Speaker-dependent systems have the adventage that the voice of the user will be analyzed and the result is an more accurate transcription.
Web search engine[edit | edit source]
A web search engine is able to intelligently search through the web by using a complex algorithm. The user inputs a search term and the search engine is able to show the most relevant information and URLs about it.
But what makes a search engine intelligent and therewith an artificial intelligence? For instance, Google (the search engine) analyses their users' search behavior and increases the accuracy of relevant search results. Nevertheless on the other hand, this intelligence decreases the privacy and makes it possible to show the user personalized advertisements which are Google’s main source of income.
Another robotic aspect of a search engine is the crawling engine which makes it possible to automatically and periodically index most of the websites available in the internet.
Chatbot[edit | edit source]
A chatbot (→chatter robot) is a type of an AI that communicates via text-based chat with the user. The first chatbot in history was “ELIZA” which was invented by Joseph Weizenbaum in the years from 1964 to 1966. With his popular invention, he tried to imitate a human psychotherapist.
The algorithm of the bot should be able to detect different word classes and categories. A "good" chatbot also needs a big database that is sorted by different patterns and categories (e.g. food, animals, emotions, etc.). Some of those chatbots are even able to answer questions for real (-time) information like “How will the weather be tomorrow?” by e.g. using another web service or script.
The intelligence of a chatbot often is combined with speech recognition (examples: Google Now, Cortana, Siri, etc.). There are also chatbots that are limited to a subject area, e.g. to only answer scientific questions or questions related to various products in an online shop automatically and replace service personal.
Examples/External Weblinks[edit | edit source]
- http://www.cleverbot.com/ (has an AI which is able to learn from human conversations and expand its vocabulary/database)
- http://www.wolframalpha.com/ (basically a scientific search engine, but it also has aspects that are similar to a chatbot)
- https://www.chatbots.org/ (a register with different chatbots)
Applications[edit | edit source]
- military - cars - multimedia (smart phones, smart tv) - telephony (hotlines)
Machine translation[edit | edit source]
Machine translation is a field of computer linguistics. Machine translation should enable software to translate text or speech from a natural language. On a simple level machine translation only substitute words from one language (e.g. german) to another language (e.g.) english. But the translation can not be good using only this technique. The software has to recognize whole phrases.
Swarm intelligence[edit | edit source]
Swarm intelligence (SI) is the collective behavior of decentralized, self-organized systems, natural or artificial. The concept is employed in work on artificial intelligence. The expression was introduced by Gerardo Beni and Jing Wang in 1989, in the context of cellular robotic systems.
Human enhancements[edit | edit source]
As Human enhancement you generally see everything that tries to improve the Human body to create new possibilities and overcome limitations be it mometarily or
Scientific Approach[edit | edit source]
Scientiest all over the world work on new ways to help out people that lost a body part. Human enhancements replace the lost body part.
Fuzzy logic[edit | edit source]
Neural networks[edit | edit source]
In Science Fiction[edit | edit source]
Science fiction media is full of types of artificial intelligence and "intelligent" robots. Often the questions of morality and consciousness are in focus. Many movies in which a AI plays a role are rather bleak with no hope for mankind or have an bad ending. A selection of important works is listed below.
Books[edit | edit source]
- I, Robot (Isaac Asimov) A series of short story's about interactions between robots and humans with a morality focus.
- 2001 A Space Odyssey (Arthur C. Clarke)
- The Cyberiad (Stanisław Lem)
- Superman -Brainiac
Movies and TV[edit | edit source]
- Jarvis a personal assistant in Iron Man movies
- Star Wars: R2D2 & C-3PO are really good examples
- Star Trek: Data as an Android
- Star Trek: The Borg - Hive
- Terminator Series
- Blade Runner
- WarGames
- Metropolis
- The Matrix trilogy
- WALL-E
- Real Humans - Hubots
- Alien Saga: Android Bishop
Video Games[edit | edit source]
- System Shock Series
- Mass Effect
- Portal
- Portal 2
In Video Games[edit | edit source]
In video games, artificial intelligence is used to generate intelligent behaviors primarily in non-player characters (NPCs), often simulating human-like intelligence.
Or as an other species like the Geth http://masseffect.wikia.com/wiki/Geth in Mass Effect
History[edit | edit source]
Games with excellent AI[edit | edit source]
- Black and White
- Creatures
- SimCity
- F.E.A.R.
- Crysis
- Half-Life 1&2
- Halo
- Civilization
- Galactic Civilization I & II
Ethics of artificial intelligence[edit | edit source]
The ethics of artificial intelligence is the part of the ethics of technology specific to robots and other artificially intelligent beings. It is typically divided into roboethics, a concern with the moral behavior of humans as they design, construct, use and treat artificially intelligent beings, and machine ethics, concern with the moral behavior of artificial moral agents (AMAs).
People[edit | edit source]
Alan Turing[edit | edit source]
Alan Mathison Turing, (23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) is considered the father of theoretical computer science and artificial intelligence. He provided a test for "intelligent" machines which tests if the response of a machine is indistinguishable from the response of a human.
Turing Test[edit | edit source]
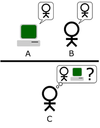
The turing test was developed 1950 by alan turing, to compare human intelligence with machine intelligence.
Advantages and disadvantages[edit | edit source]
Advantages[edit | edit source]
- Work can be much faster
- Products have a consistent quality
- Intelligent machines do hard work instead of humans.
- People are more healthy
- Dangerous work can be done more effectively.
Disadvantages[edit | edit source]
- Because machines can do more and faster human works many people lose their jobs and complete industries are nearly controlled by robots and AI systems.
- AI systems can be just as perfect as the human who creates it.
- Can only make rational decisions.
- Lack of interpersonal skills.